
by Dr. Adkins | Jun 21, 2019 | Blog, Dental Information, Dental Topics 2
Reaching for a sports drink may seem like a smart way to rehydrate during a big game or after completing your exercise regimen, but you may not be as educated as you think. Consumption of sports drinks is on the rise, with 62 percent of American teenagers drinking at least one a day. That’s why it’s important to inform consumers that these drinks which are touted to help your body can also take a toll on your health, at least on your oral health. Let’s find out exactly how sports drinks can negatively impact your teeth.
What makes sports drinks harmful?
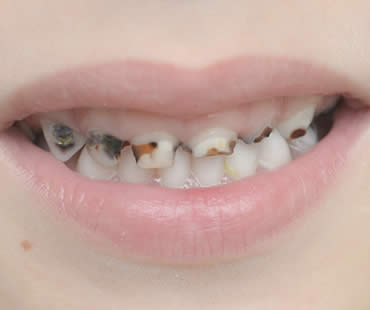
You might guess that sugar is what makes these drinks less appealing. It’s true that you should avoid the brands heavy in sugar, but that’s actually not your teeth’s biggest enemy in sports drinks. It’s the high acid content that presents the most danger. Researchers have found that sports drinks have so much acid that they can start damaging your teeth after just five days of regular consumption.
Aren’t they better than drinking soda?
Most people choose these drinks thinking they will enhance their sports performance, and that they’re a better option than soda. Sports drinks are not that different than soda because they contain as much or more sugar. It’s simply not true that sports drinks are healthier for your teeth than soda.
What kind of damage can they do?
The acid in sports drinks can cause irreversible damage to your teeth. They erode your enamel, which is the shiny outer layer of your teeth, causing them to become sensitive to temperature changes and to touch. It also increases your risk of decay and cavities.
How can I avoid harming my teeth?
If you just can’t give up sports drinks, at least try to minimize the amount you consume. Rinse your mouth with water afterwards, but don’t brush your teeth immediately because it might spread the acid around your mouth. Wait about an hour for the pH level in your mouth to normalize, and then brush. You can also chew sugarless gum after having a sports drink, which increases your saliva flow and helps to return your mouth’s acidity levels back to normal.
We look forward to seeing you in our McDonough dental office
by Dr. Adkins | Jun 7, 2019 | Blog, Dental Information, Dental Topics 2
Once you’re an adult, you don’t have to worry about cavities anymore. Right? Wrong! It’s true that you should have mastered oral hygiene techniques, but there are different factors that can contribute to cavities that weren’t a big issue during childhood. What are some of the things that put you at risk for cavities once you’ve reached adulthood, and what can you do about them?
Diet
Often your diet is worse as an adult without even realizing it, and what you eat and drink directly affects your teeth and gums. Sugar is the biggest offender and all types of sugar counts, not just the obvious candy or sodas. Limit your consumption of juices, milk, crackers, sweetened coffee, fruits, and vitamin or energy drinks.
Grazing
Many people tend to “graze” on foods and drinks all day long. If you snack frequently, you’re giving bacteria a constant supply of sugars to mix with and damage your mouth. Even though it’s tempting to sip on coffee or soda all morning, it’s better to drink it in one sitting. Also consider using a straw to avoid your teeth completely.
Receding gums
If your gums pull away from your teeth, your tooth roots can be exposed to plaque. Older patients with gingivitis, or gum disease, are more likely to form cavities. If the roots of your teeth are uncovered, you are more susceptible to plaque buildup and tooth decay.
Previous fillings
Fillings you received earlier in life can contribute to adult cavities. The filling may weaken with time, allowing bacteria into any cracks. Your dentist will check existing fillings for wear and replace them if needed.
Medical conditions
People with lower saliva flow due to various illnesses are at higher risk of cavities. Cancer patients who have undergone chemotherapy or radiation are at more risk, as are smokers. People with limited manual dexterity may be unable to clean their teeth sufficiently.
Ways to decrease your risk
Brush with a fluoride toothpaste after meals, floss daily, and rinse with a fluoride mouthwash. See your dentist twice a year, and also inquire about fluoride treatments.
We look forward to seeing you in our McDonough dental office
by Dr. Adkins | Apr 5, 2019 | Blog, Dental Information, Dental Topics 2
The word cancer strikes fear and dismay in most people, and it’s no different when the diagnosis is oral cancer. Nearly 37,000 Americans are diagnosed with this disease each year and about 8,000 succumb to it. You should know the risk factors and symptoms so that you can either avoid it completely, or catch it early enough that you’ll have the best chance of recovery.
Who is at risk?
Oral cancer is not contagious, but there are some activities that put you at higher risk for the disease. Both smoked and smokeless tobacco are linked to oral cancer, and the more you use tobacco the greater your risk becomes. Excessive alcohol consumption also increases your risk, and paired with tobacco use your risk is even higher. Sun exposure heightens your chances of developing cancer of the lip.
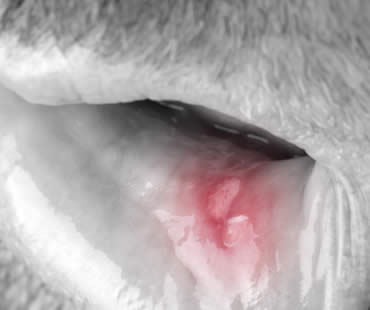
What are the symptoms?
Oral cancer patients may experience any of these signs of the disease:
- A sore in the mouth or throat that bleeds often and doesn’t heal within two weeks
- A thick area or lump in the cheek
- Patches in your mouth or on your lips that are red, white, or a mixture of the two
- Pain or difficulty swallowing
- Difficulty wearing your dentures
- A sore throat
- Tongue or mouth numbness
- Difficulty chewing, or moving your jaw or tongue
- Earache
What should I do if I have symptoms?
If you notice any of these signs, visit your dentist right away to get screened for oral cancer. When diagnosed early, there is an 80 percent survival rate. Unfortunately many patients wait too long to see their dentist, and late-stage diagnosis is the reason for most oral cancer deaths.
Our dental office is located in McDonough

by Dr. Adkins | Mar 1, 2019 | Blog, Dental Information, Dental Topics 2
Pregnancy brings many kinds of excitement and joy to a mother’s life, but gum problems aren’t one of them. Pregnancy gingivitis not only causes gum trouble, it can also lead to higher risks for preterm labor and problems with the newborn baby. If you are pregnant and notice swelling or inflammation of your gums, you might have pregnancy gingivitis. It results from plaque buildup that irritates your gums, and can harbor bacteria that gets into your body. The bacteria can travel to your uterus and affect your pregnancy and unborn child. How can you avoid pregnancy gingivitis?
Oral hygiene
Brush and floss your teeth properly. Try to brush after all meals and snacks, especially those high in sugars or starches. See your dentist for frequent cleanings, aiming for two to three times during your pregnancy. This will remove more plaque from your teeth that you can at home, serving to lower your risk for plaque buildup.
Education
Consult your dentist before, during, and after your pregnancy. You will learn how to best care for your mouth, and what to watch for in case a problem does arise.
Nutrition
Maintaining a healthy diet during pregnancy will not only benefit your overall health and that of the baby, but will also limit your sugar intake which promotes plaque formation.
Dental care
Try to have dental procedures performed before you become pregnant. Some emergency procedures are safe during pregnancy, but it is best to have treatment done before pregnancy.
Bacteria control
Avoid sharing food and utensils so that you don’t transfer bacteria from person to person. Your goal is to limit the amount of bacteria in your mouth as much as possible.
Xylitol gum
Chewing sugarless gum promotes saliva, which help equalize the acids in your mouth and fight plaque buildup. The ingredient xylitol has been shown to help prevent bacteria from being able to stick on your teeth, therefore fighting tooth decay.
If you need a dentist in McDonough contact us today

by Dr. Adkins | Dec 7, 2018 | Blog, Dental Information, Dental Topics 2
Most people turn to mouthwash when they suspect their breath is bad and they want a quick boost. It’s true that mouthwash comes in handy for this purpose, but did you know that it offers other benefits too?
Reduces bacteria
Antiseptic and anti-plaque mouth rinses are intended to kill germs that cause gum disease, plaque, and bad breath. Swishing this type of mouthwash around your mouth after brushing has been shown to lower the bacteria levels, and therefore decrease your risks of the problems that bacteria can cause. It is especially helpful in senior adults or others who have trouble brushing and flossing their teeth.
Promotes healing
Rinsing with antiseptic mouthwash promotes natural healing of mouth and gum irritations, minor wounds, and canker sores. It removes debris that can irritate your mouth, and can also help reduce inflammations from dental and orthodontic appliances.
Adds fluoride
Some rinses contain fluoride, which helps prevent tooth decay and strengthen teeth. Studies have shown that using fluoride mouth rinses in addition to fluoride toothpaste gives you more protection against cavities than toothpaste alone. Fluoride mouth rinse is not suggested for kids under six years old because they might swallow it.
Relieves pain
Antiseptic mouth rinses have been shown to help reduce tooth pain, probably due to lowering the bacteria and inflammation in your mouth.
Helps with certain conditions
Dentists sometimes prescribe special mouth rinses designed for various oral conditions. This may include gum disease, high risk of tooth decay, or dry mouth. Also, oral rinses may be prescribed after periodontal treatments or oral surgery.
Supplements dental hygiene
Many dentists suggest making dental rinses part of your oral hygiene routine, but remember that it’s only a supplement to brushing and flossing regularly.
Our dental office is located in McDonough
by Dr. Adkins | Nov 23, 2018 | Blog, Dental Information, Dental Topics 2
Sores in or around your mouth are painful and unsightly. They can have a variety of causes, such as infections, irritation from orthodontics or dentures, and symptoms of another health problem. Here are descriptions of the most common mouth sores.
Cold sores
Also called fever blisters, cold sores appear around your lips, nose, or chin. These extremely contagious, fluid-filled blisters are caused by the herpes simplex virus type 1. Once you are infected with primary herpes, the virus remains in your body and occasionally flares up. Cold sores typically heal by themselves in about a week. Over-the-counter topical anesthetics may help, and your dentist may prescribe antiviral medications to reduce occurrences.
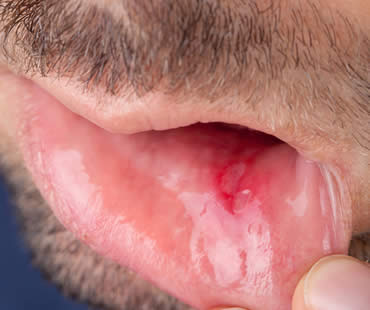
Canker sores
These small ulcers only appear inside your mouth. They are white or gray with a red border, and are not contagious. Experts are unsure of the exact cause, but suspect they are related to immune system deficiencies, viruses, or bacteria. Canker sores usually heal on their own in a week or two. It is advised to avoid spicy, hot, or acidic foods that can irritate the sore. Over-the-counter mouthwashes or topical anesthetics may help, and your dentist may prescribe antibiotics if a secondary infection occurs.
Thrush
Oral thrush, or candidiasis, is a fungal infection occurring when the yeast Candida albicans reproduces in great amounts. Common with denture wearers, it most often appears in people with weakened immune systems such as the elderly or ill. People with dry mouth or who are on antibiotics are also at greater risk for thrush. The key to controlling candidiasis is treating the condition that causes it. Dentures should be cleaned regularly and removed at bedtime, and dry mouth should be treated in an effort to lessen that condition.
Leukoplakia
Leukoplakia are thick, white patches that grow on the inside of your cheeks, gums or tongue. Common with tobacco users, they result from irritations from habits like chewing on your cheek or wearing ill-fitting dentures. Leukoplakia are also associated with oral cancer. Treatment focuses on addressing the reasons for the lesion, such as quitting smoking or replacing dentures.
If you live in the McDonough area contact us today








 (470) 665-5292
(470) 665-5292  E-Mail Us
E-Mail Us 
